- C-media Ac97 Audio Device Windows 7 32bit
- C-media Ac97 Audio Device Download
- Media Ac97 Audio Device
- Ac97 Audio Drivers Windows Xp
- Ac97 Xp Driver
- AC'97 Audio Codec AC'97 Digital Controller AC link interface Audio Codec - is the actual unit responsible for converting bits into audio signals and vice-versa. It comprises of the Digital to Analog (DAC) and Digital to Analog (ADC) converters. It gives the analog audio output on LINEOUT, AUXOUT and MONOOUT (optional). It takes in analog.
- PC Audio Codecs AC'97 Audio Codecs Software Files Windows. Download Description Version Update Time File Size; Vista/Win7 (32/64 bits) Driver only (ZIP file).
Crack vst plugins google drive. Category: Sound and Multimedia
Manufacturer: C-Media
Caution Level: Safe
Download File Size: 30.34 MiB
Operating System: Windows XP/2000/Vista
Latest Version / Release Date: 6.14.01.4080 / 04 Jan 2004
Windows device driver information for C-Media AC97 Audio Device
The C-media audio AC97 Device is a product from C-media Company. It has a latest high end computer card for sound, it features the operating system of the windows vista/ XP, it has other versions but there is a latest one, which has a noise signal ratio that is up to 120db, which is in it. It is a three dimension driver that is audio, and with these variety of technology gives a person access to change the stereo computer audio to being like experiencing a surround from the holly wood levels. The c-media audio AC97 device is the one that supports the driver that is used to install the software. It is one of the very latest inventions so it has the best technology that should possibly be achieved however with technology there is never knowing when to stop.
Outdated Drivers?
Unless you update your drivers regularly you may face hardware performance issues.
This package contains the files for installing the Realtek AC97 Audio Driver. If it has been installed, updating (overwrite-installing) may fix problems, add new functions, or expand functions. This Vinyl AC’97 Codec Combo, also known as Vinyl Audio Codec, supports all VIA southbridges with integrated sound, including VT8231/VT82C686A/VT8235/VT8237/VT8233/VT82C686B/VT8233A/VT8233C/VT8287. This driver supports the VIA Six-TRAC (VT1616 Codec).
To check your drivers you should manually verify every device on your system for driver updates

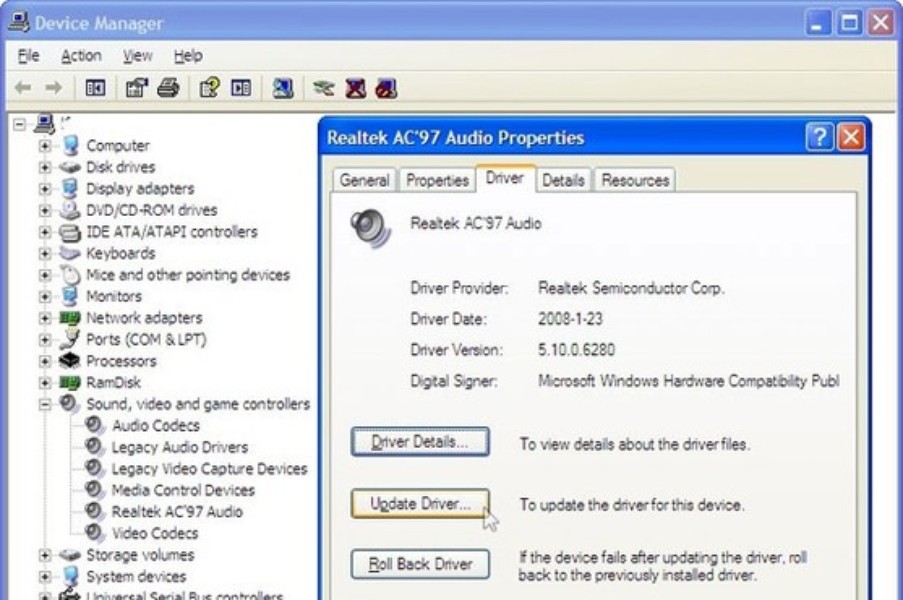
The c-media audio AC97 device can be installed by an individual following the instructions. First describe the computer model, describe the operating system that the computer is using so as a person is able to install the c-media computer device. When updating the device ensure that one is using windows vista. Go through the computer drivers, locate the C-media computer drivers, choose c-media audio AC97 device. Download the c-media audio AC97 device, and then click to install the audio device. Then switch off the computer and switch it on again so that it is able to finish with the installation in the computer. If an exclamation mark is shown in a yellow color it means that a person maybe using a wrong driver. The device can be downloaded online, using the direct download URL for the C-media audio AC97 device. It is highly recommended you run a free registry scan for Windows and C-Media AC97 Audio Device errors before installing any driver updates.

AC'97 (Audio Codec '97; also MC'97 for Modem Codec '97) is an audiocodec standard developed by Intel Architecture Labs in 1997. The standard was used in motherboards, modems, and sound cards.
The specification covers two types of component, and the 'AC-link' digital interface between them:
- an AC'97 digital controller (DC97), which is built into the southbridge of the chipset, and
- an AC'97 audio and modem codec, available from several vendors, which contains the analog components of the architecture.
AC'97 defines a high-quality, 16- or 20-bit audio architecture with 5.1 surround sound support for the PC. AC'97 supports a 96 kHz sampling rate at 20-bit stereo resolution and a 48 kHz sampling rate at 20-bit stereo resolution for multichannel recording and playback.
Integrated audio is implemented with the AC'97 Codec on the motherboard, a Communications and Networking Riser card, or an audio/modem riser card.
In 2004, Intel released Intel High Definition Audio (HD Audio) which is a successor that is not backward compatible with AC'97.[1] HD Audio has the capability to define up to 15 output channels, but in practice most motherboards provide no more than 8 channels (7.1 surround sound).
Revisions[edit]
AC'97 has had several revisions:[2]
- AC'97 1.x compliant indicates fixed 48K sampling rate operation (non-extended feature set)
- AC'97 2.1 compliant indicates extended audio feature set (optional variable rate, multichannel, etc.)
- AC'97 2.2 compliant indicates extended audio, enhanced riser audio support, and optional Sony/Philips Digital Interface Format
- AC'97 2.3 compliant indicates extended configuration information and optional jack sensing support
AC'97 revision 2.3 enables Plug and Play for the end user. This revision provides means for the audio codec to supply parametric data about its analog interface much like Intel High Definition Audio.
AC-Link[edit]
The AC-Link is a digital link that connects the DC97 (the controller) with the audio 'codecs.' It is composed of five wires: the 12.288 MHz clock, a 48 kHz sync signal, a reset signal, and two data wires which carry the actual audio data: sdata_out and sdata_in. The first four are outputs from the controller, while sdata_in carries input from the codec. The link carries a bidirectional serial data stream at a fixed bitrate (12.288 Mbit/s) between the controller and one or more codecs.
Each 12.288 Mbit/s stream is divided into 256-bit frames (frame frequency is 48 kHz). This is therefore a time-division multiplexing scheme.
Every frame is subdivided in 13 slots. The first (slot 0) is 16 bits long and contains validity flags for the remaining slots, while the remaining 240 bits are divided in twelve 20-bit slots (slots 1–12), used as data slots. Incardex producer.
Slots 1, 2 and 12 are used for non-audio data, while slots 3–11 carry up to nine channels of raw pulse-code modulation audio signals. Normally, six channels are used for 5.1 surround sound, and three channels are available for modem use. However, slots can be combined to provide a 96 kHz sampling rate for the L, R and C channels.
Lower sample rates (such as 44.1 kHz) are implemented using a handshake protocol between the controller and codec which skips data during certain frames. (This capability depends on the codec. Alternatively, sample rate conversion could be performed in the DC97 (controller) or in the software driver.)
Codec chips[edit]
Codec chips have an AC'97 interface on one side and analog audio interface on the other. They are usually small square chips with 48 pins (48-pin QFP package). They are D/A and A/D or only D/A.
- Analog Devices AD1819B, 1881A, 1885, 1886, 1887, 1980, 1981, 1985
- AKM (Asahi Kasei Microsystems) AK 4540, 4543, 4544A, 4545
- Avance Logic (now Realtek) ALC201A, ALC202/A, ALC650, ALC655, ALC658, ALC101, ALC202A, ALC250, ALC850, ALC888
- Conexant Cx20468 - with a modem
- Cirrus Logic CrystalWare 4236, CrystalClear SoundFusion CS4297, CS4299
- Crystal Semiconductors CS4205, CS4202
- C-Media CMI9738, 9739, 9761, 9880
- ESS ES1988 (with a modem)
- Empia EMP202 (2 channel, 20-bit DAC and 20-bit ADC, full duplex AC'97 2.2 compatible stereo audio CODEC)
- Intersil HMP9701 (obsolete, 48 kHz fixed samplerate)
- National Semiconductor LM4550, LM49321, LM49350, LM49352
- Philips UCB 1400 (with touchscreen controller)
- Realtek ALC5610 ALC5611[3][4][5]
- SigmaTel (now IDT) C-Major STAC 9460 (D/A only), 9461, 9462, 9463, 9200, 9202, 9250, 9251, 9220, 9221, 9223, 9750
- Silicon Image Si3024 (mono only)
- TriTech Microelectronics TR28022, 28026
- Yamaha YMF 743, 752, 753
- VIA VT1612, VT1616 (VIA Six-TRAC Vinyl Audio), VT82C686
- Winbond W83971
- Wolfson Microelectronics WM9701, WM9703, WM9704, WM9705 (w/touchscreen), WM9707, WM9708, WM9709 (DAC only), WM9711, WM9712 (w/touchscreen), WM9713 (w/touchscreen), WM9714
Front panel connector[edit]
Computer motherboards often provide a connector to bring microphone and headphone signals to the computer's front panel with standard color jack. Intel provides a specification for that header; the signal assignments are different for AC'97 and Intel High Definition Audioheaders.[6]
Operating system support[edit]
AC'97 is supported by most operating systems, such as Windows and Linux. Under DOS, applications access the sound hardware directly instead of through the operating system, and most DOS applications do not support AC'97. 64-bit versions of Windows 7 and later require a third-party driver for AC'97 support.[7]
C-media Ac97 Audio Device Windows 7 32bit
See also[edit]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to AC'97. |
C-media Ac97 Audio Device Download
- I²S (Integrated Interchip Sound)
References[edit]
Media Ac97 Audio Device

Ac97 Audio Drivers Windows Xp
- ^'1.2.1 AC'97 Compatibility'(PDF), High Definition Audio Specification, Revision 1.0a, Intel Corporation, 2010, p. 17
- ^Audio Codec '97(PDF), Revision 2.3 Rev 1.0 [sic], Intel Corporation, April 2002CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link)
- ^AC'97 InterfaceArchived March 2, 2012, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ALC5610 datasheet V1.4[permanent dead link]
- ^ALC5611 datasheet v1.3[permanent dead link]
- ^Intel Corporation (February 2005), Front Panel I/O Connectivity Design Guide(PDF), Version 1.3, pp. 19–25, archived from the original(PDF) on 2011-05-11, retrieved 2008-02-06
- ^VirtualBox Bug #5332, Oracle Corporation, 2009